Page 46 - INCOLA EXCLUSIVE DATA CATALOGUE
P. 46
System Design and Installation
5.11 Dew point
Dew point is a measure used to express moisture in the air. As the air cools, enough energy is
released from the water vapor and begins to condense, that is, to liquefy. This process is the
opposite of evaporation. Just as water turns into steam with sufficient energy while evaporating,
energy is lost during condensation and turns into water again. The temperature at which the
water turns from vapor to liquid again is the dew point degree.
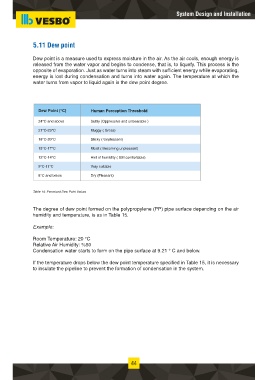
Dew Point (°C) Human Perception Threshold
24°C and above Sultry (Oppressive and unbearable )
21°C-23°C Muggy ( Gross)
18°C-20°C Sticky ( Unpleasant)
15°C-17°C Moist ( Becoming unpleasant)
12°C-14°C Hint of humidity ( Still comfortable)
9°C-11°C Very suitable
8°C and below Dry (Pleasant)
Table 14: Perceived Dew Point Values
The degree of dew point formed on the polypropylene (PP) pipe surface depending on the air
humidity and temperature, is as in Table 15.
Example:
Room Temperature: 20 °C
Relative Air Humidity: %50
Condensation water starts to form on the pipe surface at 9.21 ° C and below.
If the temperature drops below the dew point temperature specified in Table 15, it is necessary
to insulate the pipeline to prevent the formation of condensation in the system.
44